When Heather Woock was in her late 20s, she started researching her family history. As part of the project, she spit into a tube and sent it to Ancestry, a consumer DNA testing service. Then, in 2017, she started getting messages about the results from people who said they could be half siblings.
“I immediately called my mom and said, ‘Mom, is it possible that I have random siblings out there somewhere?'” Woock said. She recalled her mom responded, “No, why? That’s ridiculous.”
But the messages continued, and some of them mentioned an Indianapolis fertility practice that she knew her mom had consulted when she had trouble conceiving.
Woock researched and finally learned the truth. Dr. Donald Cline, the fertility doctor her mother saw in 1985, is her biological father.
“I went through an identity crisis,” she said. “I couldn’t look in the mirror and think about, ‘Where did my eyes come from? Where did my hair color come from?’ I didn’t even want to think about any of that.”
Woock hadn’t known that her mom had used artificial insemination to conceive her, and neither of them knew the doctor had used his own sperm.
“We now know Cline used his own sample and squirted it into my mom,” Woock said.
In the 1970s and ’80s, Cline deceived dozens of patients and used his sperm to impregnate them. He has more than 60 biological children — and counting.
For Woock, as the story of her parentage sunk in, it was distressing for another reason: She wanted to start her own family and was having trouble conceiving. And now she needed to turn to the fertility industry that had so badly betrayed her mom.
“We were doing all of the calendaring … everything that is out there to help you get pregnant, we were doing that,” Woock recalled.
But after six months, when she still wasn’t pregnant at 32, she went to a fertility clinic for some tests.
“I had to fill out all this paperwork, and there’s a slot that says kind of like, ‘Is there anything else you’d like to share?’ ” Woock said.
Yes, there most certainly was.
The Odds Of ‘Fertility Fraud’ These Days
New allegations of doctors using their own sperm keep coming to light — because of genetic-testing services like Ancestry revealing networks of half siblings — in states like Idaho, Ohio, Colorado and Arkansas.
But those doctors performed artificial inseminations decades ago. Could what happened to Woock’s mom happen in a modern fertility clinic?
Dr. Bob Colver, a fertility specialist in Carmel, Indiana, said it’s a question many of his patients have asked. But it’s unlikely, he said. These days, there are more people involved in the process, and in vitro fertilization happens in a lab, not an exam room.
“Unless you’re in a small clinic where there’s absolutely no checks and balances, I can’t even imagine that today,” Colver said.
It’s now illegal in Indiana, Texas and California for a doctor to use his sperm to impregnate his patients. But there’s no national law criminalizing what’s called “fertility fraud.”
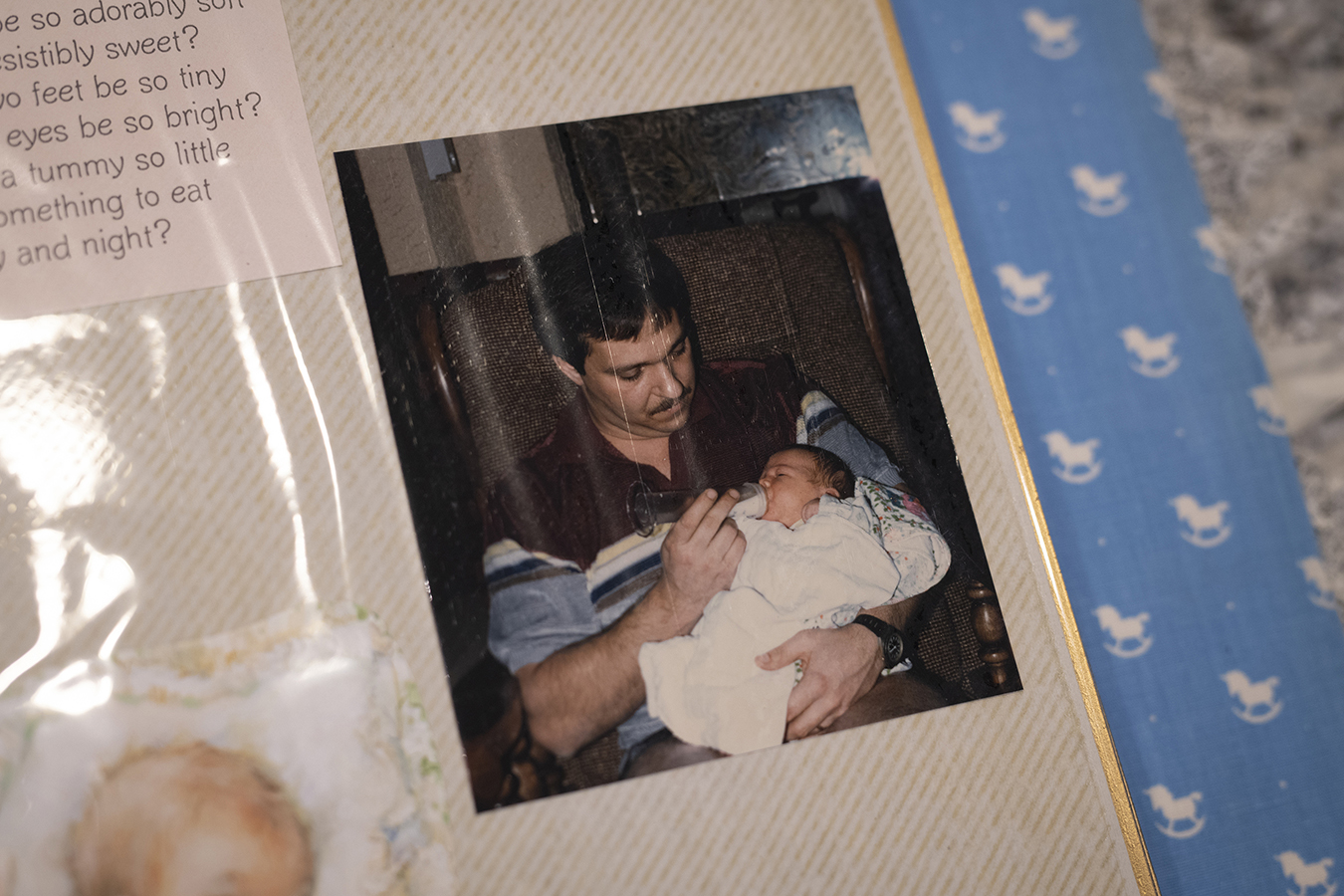

A photo of Larry Hobson holding his daughter, Heather Woock, as an infant. Woock’s mother consulted with a fertility doctor when she was having trouble getting pregnant. (Leah Klafczynski for NPR)
Fertility medicine has advanced a lot since the 1980s, but women trying to get pregnant today with the help of medicine face a baffling array of treatment options that can be hard to navigate and can be hugely expensive. And some critics say the growing, multibillion-dollar fertility industry needs more regulation.
For example, sperm banks may not get accurate medical histories from their donors, who could pass along genetic diseases. And there’s no limit on how many times a donor’s sperm can be used, which some donor children worry could increase the chance of inbreeding. Sperm donation guidelines from organizations like the American Society for Reproductive Medicine are voluntary. There was a contestant on “The Bachelorette” last year who said his sperm had helped father more than 100 kids.
Unrealistic Expectations
When Woock decided to get her first fertility treatment, she set preconditions with the clinic. She insisted on having a female doctor and insisted that a doctor be in the room for all appointments and oversee everything that happened.
Her experience with her clinic was very different from her mother’s with Cline, but nonetheless there were surprises along the way.
The clinic told her that her problems conceiving could be because of husband Rob’s low sperm count and motility (meaning his sperm weren’t great swimmers). They advised a form of in vitro fertilization that involved injecting one sperm directly into one of her eggs in a petri dish.
When doctors told Woock she needed IVF, she felt pretty optimistic.
“I’m thinking going into this that our chances of success are 70, 75%,” Woock said.
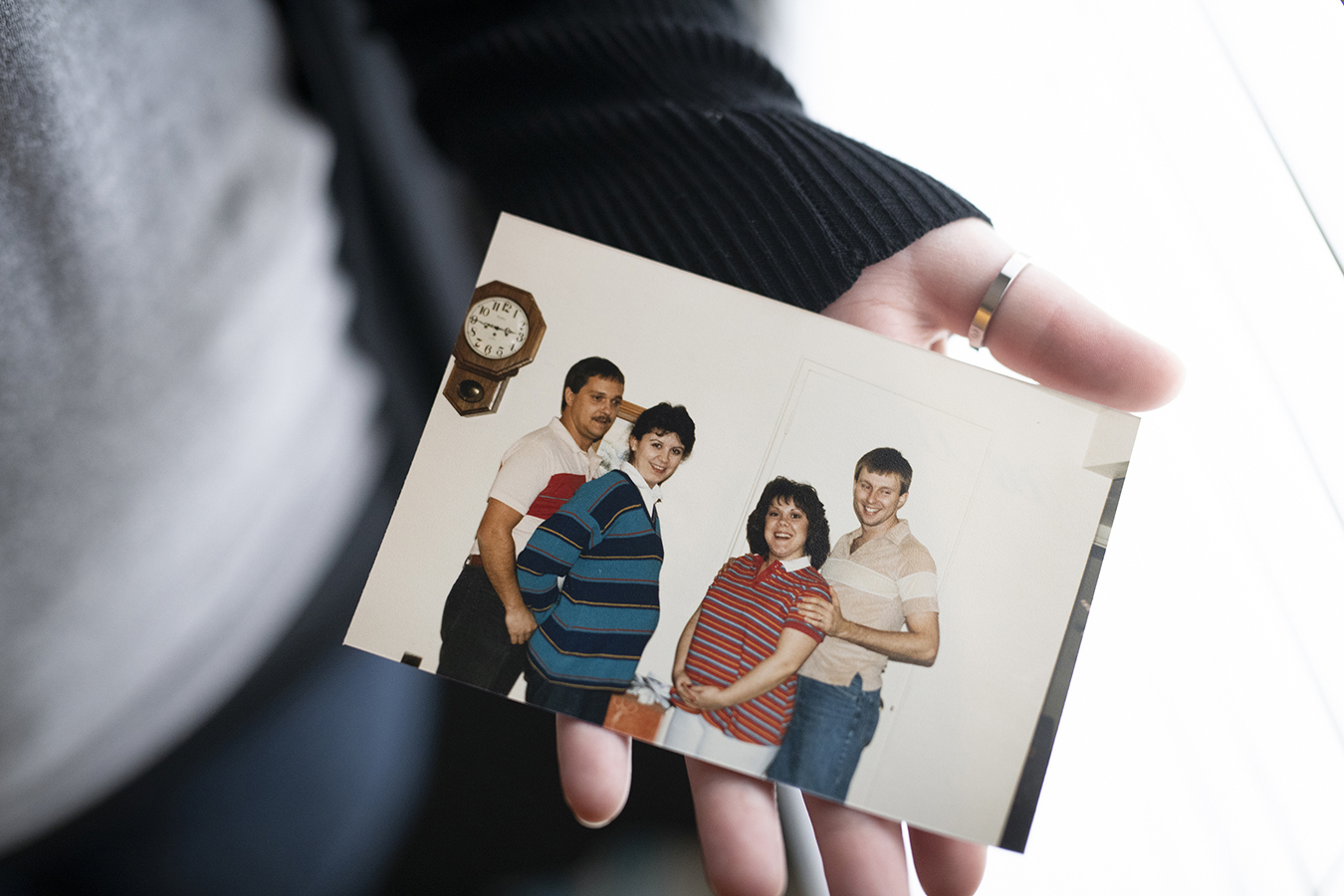

A 1985 photo of Kimberly Hobson (left) pregnant with her daughter, Heather. Kimberly is photographed alongside her husband, Larry Hobson, as well as relatives who were also expecting. (Leah Klafczynski for NPR)
Fertility treatment can be really expensive, and patients may start treatment with unrealistic expectations. That’s because success rates are complicated, and some clinics use only the best numbers in their advertising.
For example, clinics can advertise high fertilization rates. But a 70% fertilization rate doesn’t mean 70% of eggs turn into babies — plenty can go wrong after the lab combines egg and sperm.
Success depends on your age, your clinic and the type of procedure you need. But most of the time, assisted reproduction procedures such as IVF don’t work. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which tracks assisted reproduction rates in the U.S., reports only about 24% of attempts result in a baby.
‘Add-On’ Technology — And Prices
When Woock started her first IVF cycle, she gave herself shots, a couple a day, to stimulate her ovaries to get multiple eggs ready at once. Multiple eggs means more chances for fertilization.
But the drugs have side effects. They gave her headaches and made her moody and less patient.
“I was actually allergic to one of the medications, which just means that you keep taking it and deal with the itching and rash,” Woock said.
But she hung on until it was time for a doctor to surgically retrieve her eggs, at which point patients can face even more choices. Because the couple’s fertility problem appeared to be with Rob’s sperm, the clinic offered to use a special device to help pick the best sperm for IVF.
“We were kind of like yeah, ‘Why wouldn’t you?'” Woock said. “If it’s gonna give us a better chance, do it.”
A device like that is called an add-on. Add-ons are often new technology, described as cutting-edge, which can appeal to patients. Examples of add-ons include genetic testing for chromosomal abnormality in embryos — which some specialists argue improve the odds of a live birth — and assisted hatching and endometrial scratching, both methods claiming to facilitate implantation.
An exam table at Midwest Fertility Specialists, a fertility clinic in Carmel, Indiana. (Lauren Bavis/WFYI)
Jack Wilkinson, a biostatistician at the University of Manchester, researches add-ons, which he has found can increase costs — and, he said, they may not work.
“We quite often see there’s no benefit at all,” Wilkinson said. “Or, possibly even worse, that there’s a disadvantage of using that treatment.”
Wilkinson said the device Woock’s clinic offered could work, but the evidence supporting it is thin.
Failed Fertilizations
The clinic called Woock the morning after her egg retrieval. None of Woock’s eggs fertilized. The procedure revealed that her husband’s sperm quality wasn’t the only fertility issue the couple faced.
“They immediately saw that there was something wrong with my eggs,” Woock said. “My eggs are just total crap.”
She underwent a second round of IVF with the same result — no fertilization.
“Getting that news the second time … felt even more set in stone that this was going to be a very long, challenging road,” Woock said.
Challenging and expensive. Most states, including Indiana, don’t require insurers to cover fertility treatment. Without insurance, a round of IVF can cost more than $10,000 — even more than $20,000 — with no guarantee the patient will get pregnant.
Woock was lucky that her employer-provided insurance covered a lot. But it still wasn’t cheap. She had to pay for some medications, “plus, you have to pay lab and facility fees that insurance doesn’t pay,” Woock said.
Donor sperm and eggs aren’t generally covered, either. Those can be tens of thousands of dollars.
Woock faced a hard choice: After two failed attempts, did she want a kid enough to go through IVF again? She and her husband decided they did. So Woock did a third round of IVF. And then a fourth. When that didn’t work, she gave up on using her own eggs.
“What I expected as I was growing up and picturing my children is not what I will see,” Woock said.
Woock and her husband decided to try donor eggs. If all goes according to plan, she could still carry a child. She wants to keep trying.
“I realize that pregnancy is incredibly challenging on your body and your mental state,” she said. “If I can make it through a year of IVF, I can make it through morning sickness.”
This story is part of a partnership that includes Side Effects Public Media, NPR and Kaiser Health News, an editorially independent program of the Kaiser Family Foundation. The story was adapted from episode 6 of the podcast Sick. You can hear more about the fallout from Dr. Donald Cline’s deception on Sick’s first season, at sickpodcast.org.


