WINTERSET, Iowa — For 35 years, this town’s residents have brought all manner of illnesses, aches, and worries to Kevin de Regnier’s storefront clinic on the courthouse square — and he loves them for it.
De Regnier is an osteopathic physician who chose to run a family practice in a small community. Many of his patients have been with him for years. Many have chronic health problems, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or mental health struggles, which he helps manage before they become critical.
“I just decided I’d rather prevent fires than put them out,” he said between appointments on a recent afternoon.
Broad swaths of rural America don’t have enough primary care physicians, partly because many medical doctors prefer to work in highly paid specialty positions in cities. In many small towns, osteopathic doctors like de Regnier are helping fill the gap.
Osteopathic physicians, commonly known as DOs, go to separate medical schools from medical doctors, known as MDs. Their courses include lessons on how to physically manipulate the body to ease discomfort. But their training is otherwise comparable, leaders in both wings of the profession say.
Both types of doctors are licensed to practice the full range of medicine, and many patients would find little difference between them aside from the initials listed after their names.
DOs are still a minority among U.S. physicians, but their ranks are surging. From 1990 to 2022, their numbers more than quadrupled, from fewer than 25,000 to over 110,000, according to the Federation of State Medical Boards. In that same period, the number of MDs rose 91%, from about 490,000 to 934,000.
Over half of DOs work in primary care, which includes family medicine, internal medicine, and pediatrics. By contrast, more than two-thirds of MDs work in other medical specialties.
The number of osteopathic medical schools in the U.S. has more than doubled since 2000, to 40, and many of the new ones are in relatively rural states, including Idaho, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. School leaders say their locations and teaching methods help explain why many graduates wind up filling primary care jobs in smaller towns.
De Regnier noted that many MD schools are housed in large universities and connected to academic medical centers. Their students often are taught by highly specialized physicians, he said. Students at osteopathic schools tend to do their initial training at community hospitals, where they often shadow general practice doctors.
U.S. News & World Report ranks medical schools based on the percentage of graduates working in rural areas. Osteopathic schools hold three of the top four spots on the 2023 edition of that list.
William Carey University’s osteopathic school, in Hattiesburg, Mississippi, is No. 1 in that ranking. The program, which began in 2010, was intentionally sited in a region that needed more medical professionals, said Dean Italo Subbarao.
After finishing classwork, most William Carey medical students train in hospitals in Mississippi or Louisiana, Subbarao said. “Students become part of the fabric of that community,” he said. “They see the power and the value of a what a primary care doc in a smaller setting can have.”
Leaders from both sides of the profession say tension between DOs and MDs has eased. In the past, many osteopathic physicians felt their MD counterparts looked down on them. They were denied privileges in some hospitals, so they often founded their own facilities. But their training is now widely considered comparable, and students from both kinds of medical schools compete for slots in the same residency training programs.
Michael Dill, director of workforce studies at the Association of American Medical Colleges, said it makes sense that osteopathic school graduates are more likely to go into family practice, internal medicine, or pediatrics. “The very nature of osteopathic training emphasizes primary care. That’s kind of their thing,” said Dill, whose group represents MD medical schools.
Dill said he would be confident in the care provided by both types of doctors. “I would be equally willing to see either as my own primary care physician,” he said.
Data from the University of Iowa shows osteopathic physicians have been filling rural roles previously filled by medical doctors. The university’s Office of Statewide Clinical Education Programs tracks the state’s health care workforce, and its staff analyzed the data for KFF Health News.
The analysis found that, from 2008 to 2022, the number of Iowa MDs based outside the state’s 11 most urban counties dropped more than 19%. Over the same period, the number of DOs based outside those urban areas increased by 29%. Because of the shift, DOs now make up more than a third of rural Iowa physicians, and that proportion is expected to grow.
In Madison County, the picturesque rural area where de Regnier practices, the University of Iowa database lists seven physicians practicing family medicine or pediatrics. All are DOs.
De Regnier, 65, speculated that the local dominance of the osteopathic profession is partly due to the proximity of his alma mater, Des Moines University, which runs an osteopathic training center 35 miles northeast of Winterset.
Des Moines University has one of the country’s oldest osteopathic medical schools. It graduates about 210 DO students a year, compared with about 150 MD students who graduate annually from the University of Iowa, home to the state’s only other medical school.
Many patients probably pay no attention to whether a physician is an MD or a DO, but some seek the osteopathic type, said de Regnier, who is a past president of the American College of Osteopathic Family Physicians. Patients might like the physical manipulation DOs can use to ease aches in their limbs or back. And they might sense the profession’s focus on patients’ overall health, he said.
On a recent afternoon, de Regnier worked his way through a slate of patients, most of whom had seen him before.
One of them was Ben Turner, a 76-year-old pastor from the nearby town of Lorimor. Turner had come in for a check of his diabetes. He sat on the exam table with his shoes off and his eyes closed.
De Regnier took out a flexible plastic probe and instructed Turner to say when he felt it touch his feet. Then the doctor began to gently place the probe on the patient’s skin.
“Yup,” Turner said as the probe glanced against each toe. “Yup,” he said as de Regnier brushed the probe against his soles and moved to the other foot. “Yeah. Yeah. Yup. Yeah.”
The doctor offered good news: Turner had no signs of nerve damage in his feet, which is a common complication of diabetes. A blood sample showed he had a good A1C level, a measure of the disease. He had no heaviness in his chest, shortness of breath, or wheezing. Medication appeared to be staving off problems.
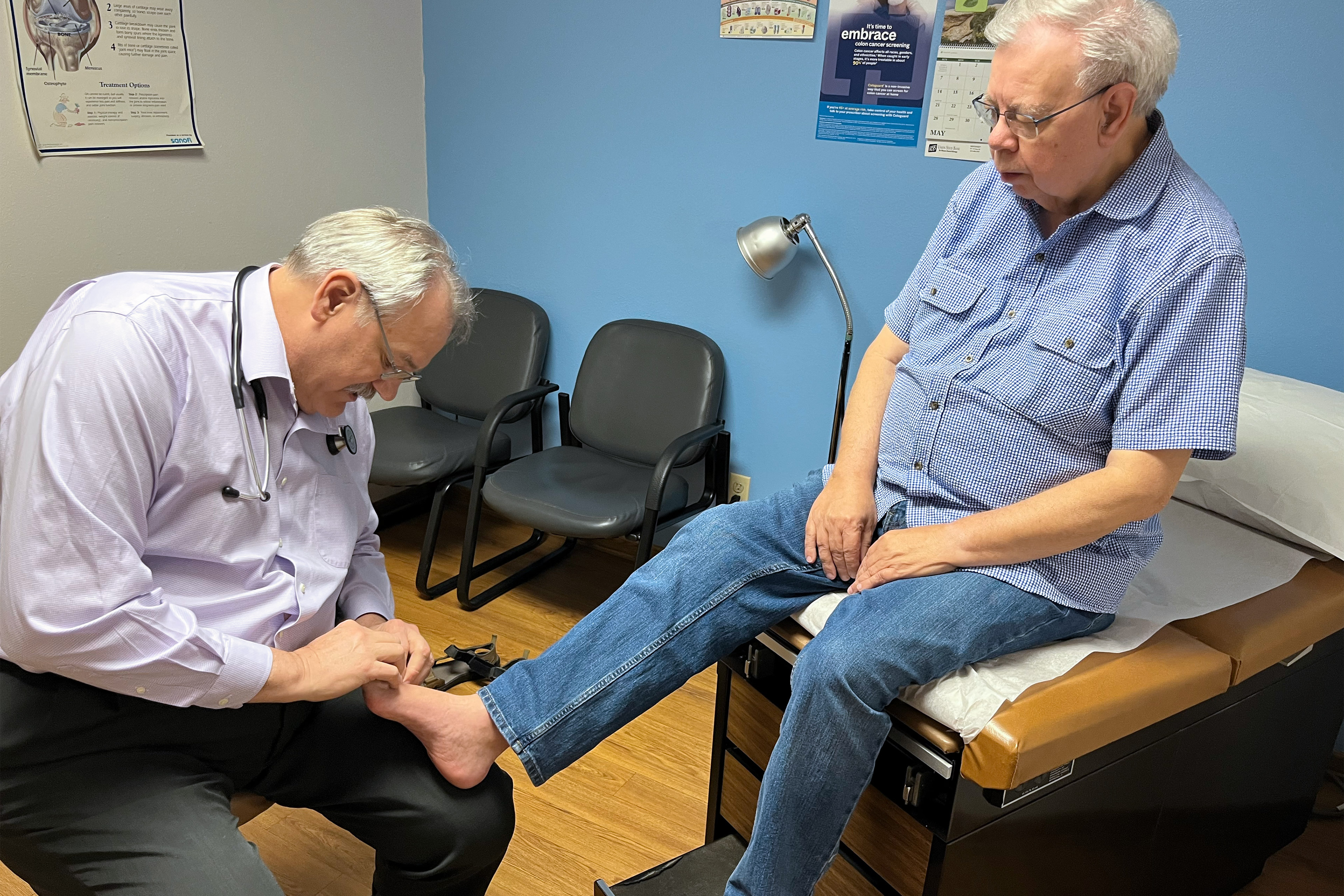
Chris Bourne, 55, of Winterset, stopped in to consult de Regnier about his mental health. Bourne has been seeing de Regnier for about five years.
Bourne takes pills for anxiety. With input from the doctor, he had reduced the dose. The anxious feelings crept back in, and he had trouble sleeping, he told de Regnier, sounding disappointed.
De Regnier noted the dose he prescribed to Bourne is relatively low, but he had approved of the attempt to reduce it. “I’m glad you tried,” he said. “Don’t beat yourself up.”
In an interview later, Bourne said that until he moved to Winterset five years ago, he’d never gone to an osteopathic physician — and didn’t know what one was. He’s come to appreciate the patience de Regnier shows in determining what might be causing a patient’s problem.
“When he sits down on that stool, he’s yours,” Bourne said.
Another patient that day was Lloyd Proctor Jr., 54, who was suffering from previously undiagnosed diabetes. His legs were swollen, and he felt run-down. Tests showed his blood sugar was more than four times the normal level.
“The pancreas isn’t happy right now, because it’s working too hard trying to take care of that blood sugar,” the doctor told him.
De Regnier diagnosed him with diabetes and prescribed medication and insulin, saying he would adjust the order if necessary to minimize Proctor’s costs after insurance. He brought out a syringe and showed Proctor how to give himself insulin injections. Proctor listened to advice on how to measure blood sugar.
“And maybe I should quit grabbing Mountain Dew every time I’m thirsty,” the patient said, ruefully.
De Regnier smiled. “I was just getting to that,” he said.
The appointment was one of the doctor’s longest of the day. At the end, he reassured Proctor that they could get his diabetes under control together.
“I know that’s a lot of info. If you get home and think, ‘What’d he say?’ — don’t hesitate to pick up the phone and give me a call,” de Regnier said. “I’m happy to visit anytime.”
This article was produced by KFF Health News, a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF — the independent source for health policy research, polling, and journalism.